Our Work
Browse a selection of Carnevale Associates Policy & Issue Briefs, conference presentations, and longer policy reports -- covering behavioral health and criminal justice issues.
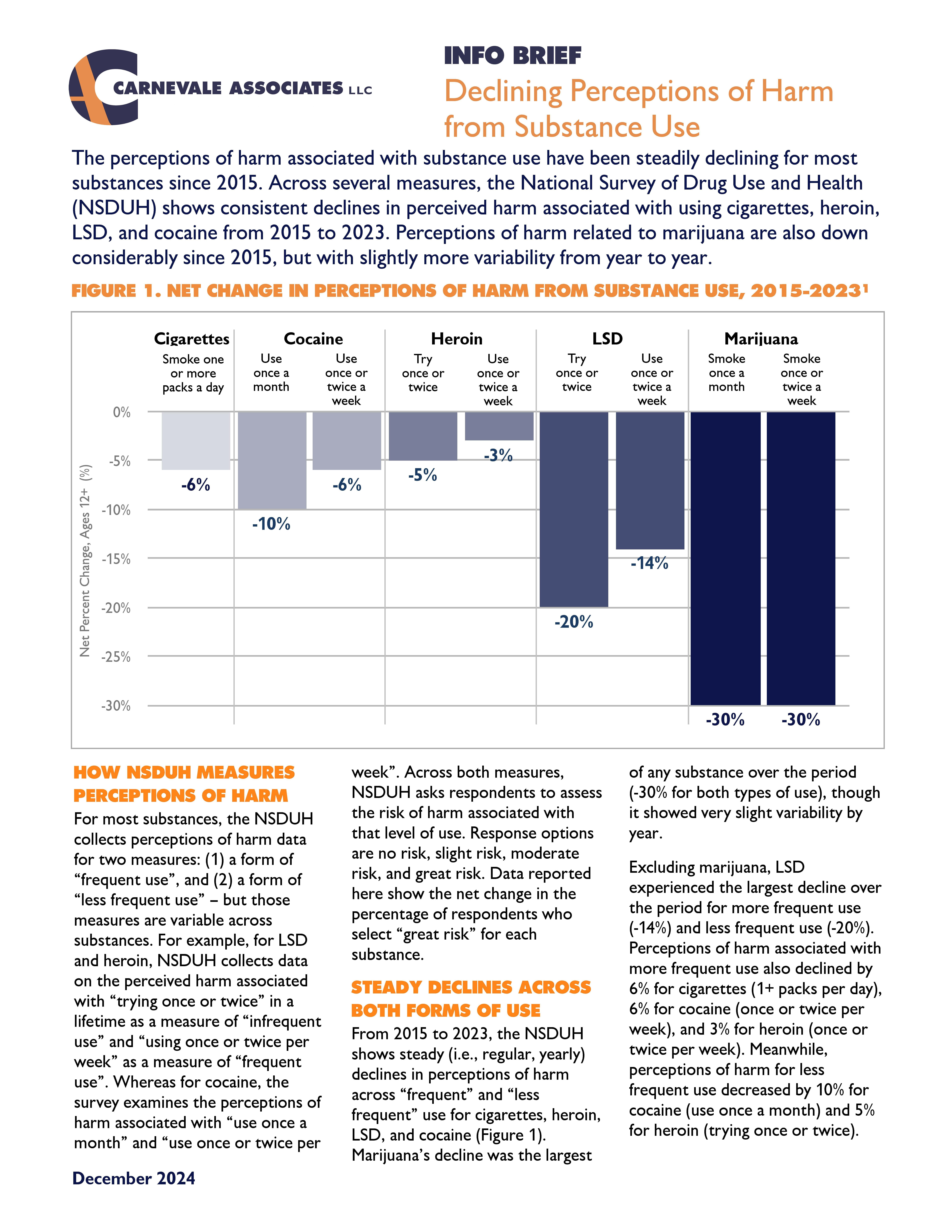
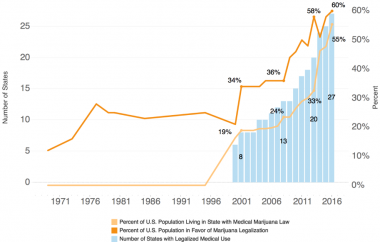
The perceptions of harm associated with substance use have been steadily declining for most substances since 2015. Across several measures, the National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) shows consistent declines in perceived harm associated with using cigarettes, heroin, LSD, and cocaine from 2015 to 2023. Perceptions of harm related to marijuana are also down considerably since 2015, but with slightly more variability from year to year.
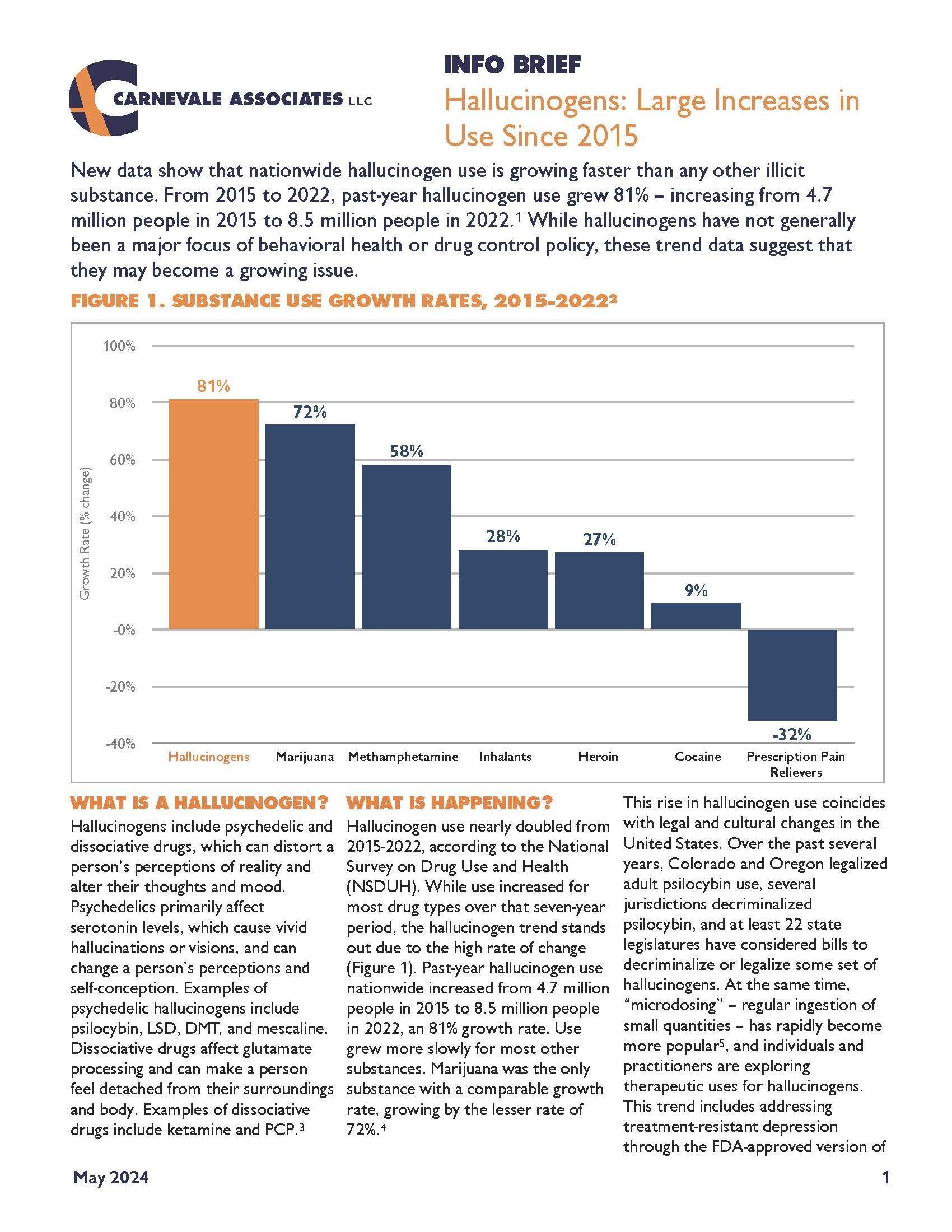
New data show that nationwide hallucinogen use is growing faster than any other illicit substance. From 2015 to 2022, past-year hallucinogen use grew 81% – increasing from 4.7 million people in 2015 to 8.5 million people in 2022. While hallucinogens have not generally been a major focus of behavioral health or drug control policy, these trend data suggest that they may become a growing issue.
Substance misuse and trauma are tightly linked. A holistic approach to prevention and treatment requires understanding, acknowledging, and addressing trauma. This brief explores what trauma is, how it relates to substance misuse, and strategies to better address both issues together.
This brief provides an update to the status of state cannabis laws in the United States, following the November 2023 election. Although cannabis remains illegal at the federal level, 38 states and the District of Columbia have now legalized medical cannabis use, with 25 of those jurisdictions also legalizing non-medical (i.e., recreational) cannabis use. Overall, almost 74% of U.S. residents now live in a state with legalized medical or non-medical cannabis use.
Delivered in conjunction with the Danya Institute at the National Prevention Network Conference on August 17, 2023 in Birmingham, Alabama.
Xylazine is an emerging issue across the United States. This presentation summarizes the available research and data on xylazine use for public health professionals, specifically in the context of broader substance use prevention.
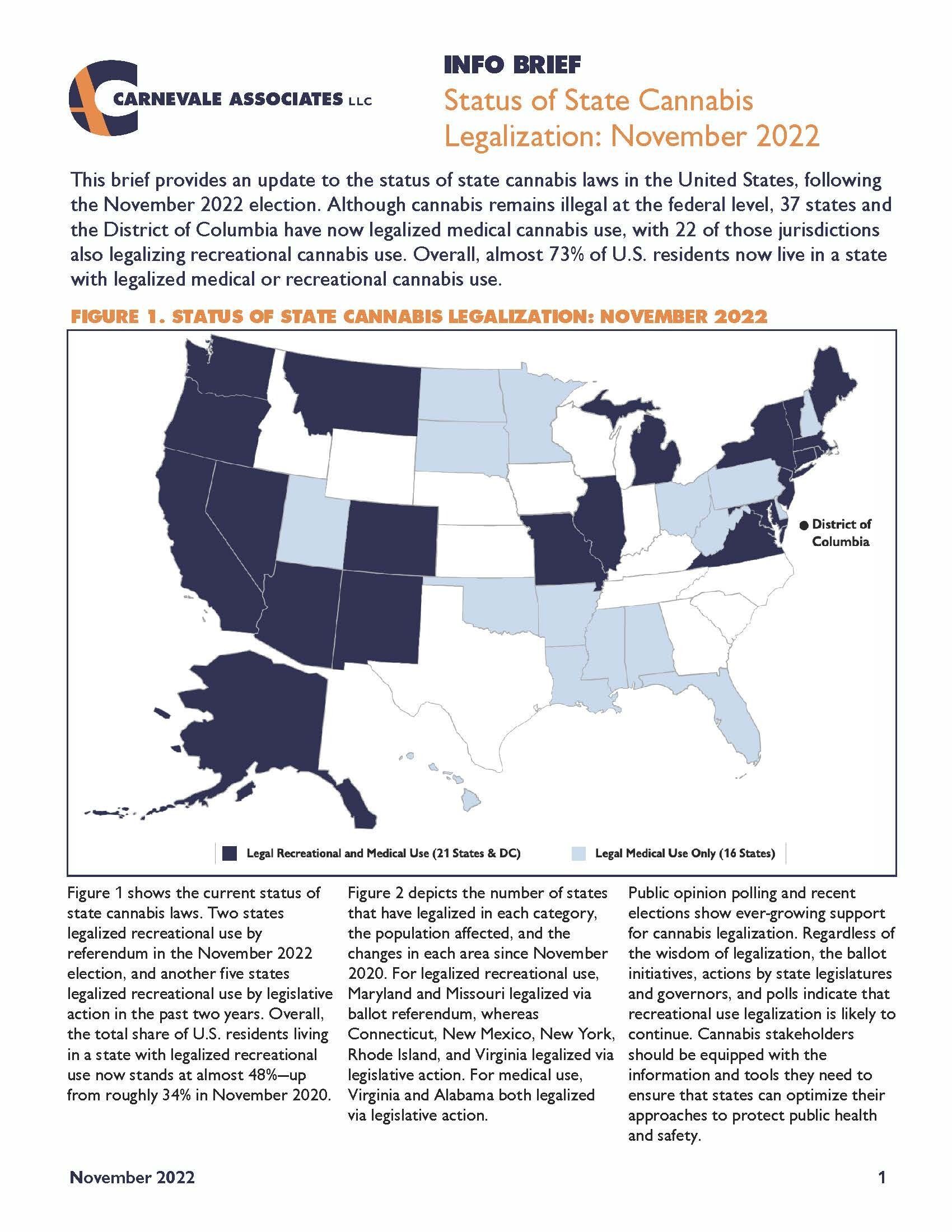
This brief provides an update to the status of state cannabis laws in the United States, following the November 2022 election. Although cannabis remains illegal at the federal level, 37 states and the District of Columbia have now legalized medical cannabis use, with 22 of those jurisdictions also legalizing recreational cannabis use. Overall, almost 73% of U.S. residents now live in a state with legalized medical or recreational cannabis use.
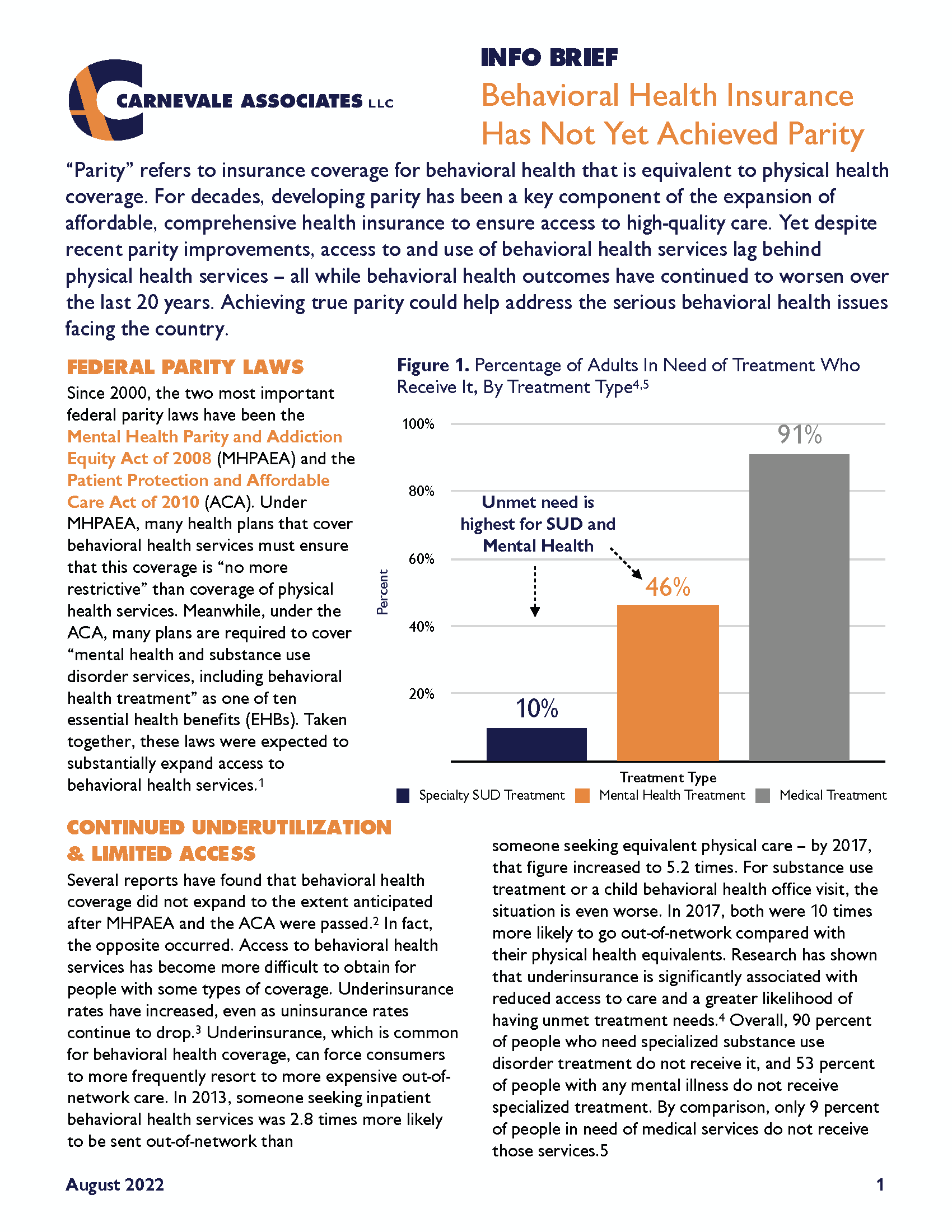
“Parity” refers to insurance coverage for behavioral health that is equivalent to physical health coverage. For decades, developing parity has been a key component of the expansion of affordable, comprehensive health insurance to ensure access to high-quality care. Yet despite recent parity improvements, access to and use of behavioral health services lag behind physical health services – all while behavioral health outcomes have continued to worsen over the last 20 years. Achieving true parity could help address the serious behavioral health issues facing the country.
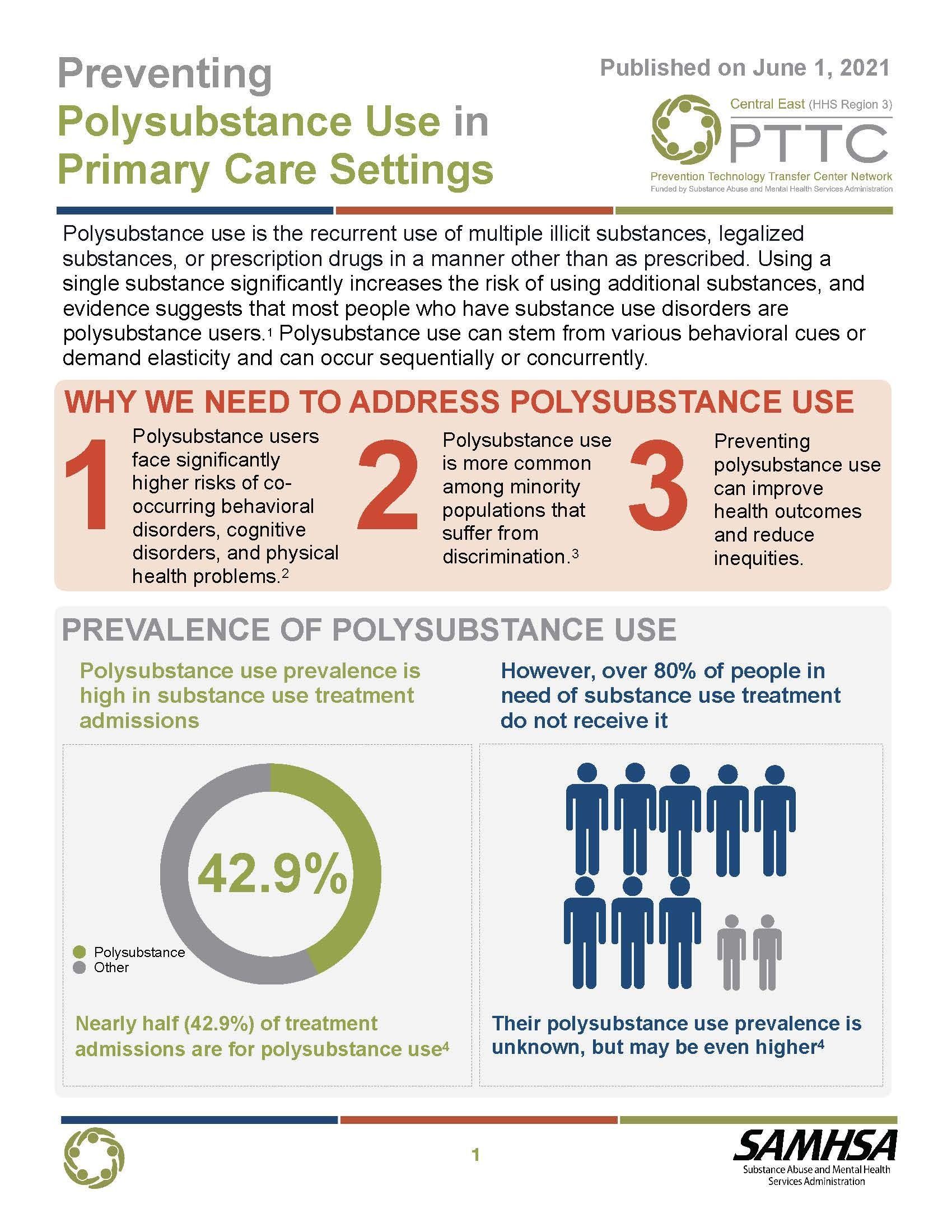
Produced on behalf of the Central East Prevention Technology Transfer Center (PTTC), this infographic illustrates the importance of polysubstance use prevention. It identifies primary care providers as a key partner for prevention and visualizes the ways they can help address polysubstance use. It was designed to serve as an introduction to the topic for new staff, partners, or other stakeholders.
Original publication date: June 1, 2021
Produced on behalf of the Central East Prevention Technology Transfer Center, this infographic illustrates the importance of polysubstance use prevention. It identifies primary care providers as a key partner for prevention and visualizes the ways they can help address polysubstance use. It was designed to serve as an introduction to the topic for new staff, partners, or other stakeholders.
Original publication date: February 25, 2020
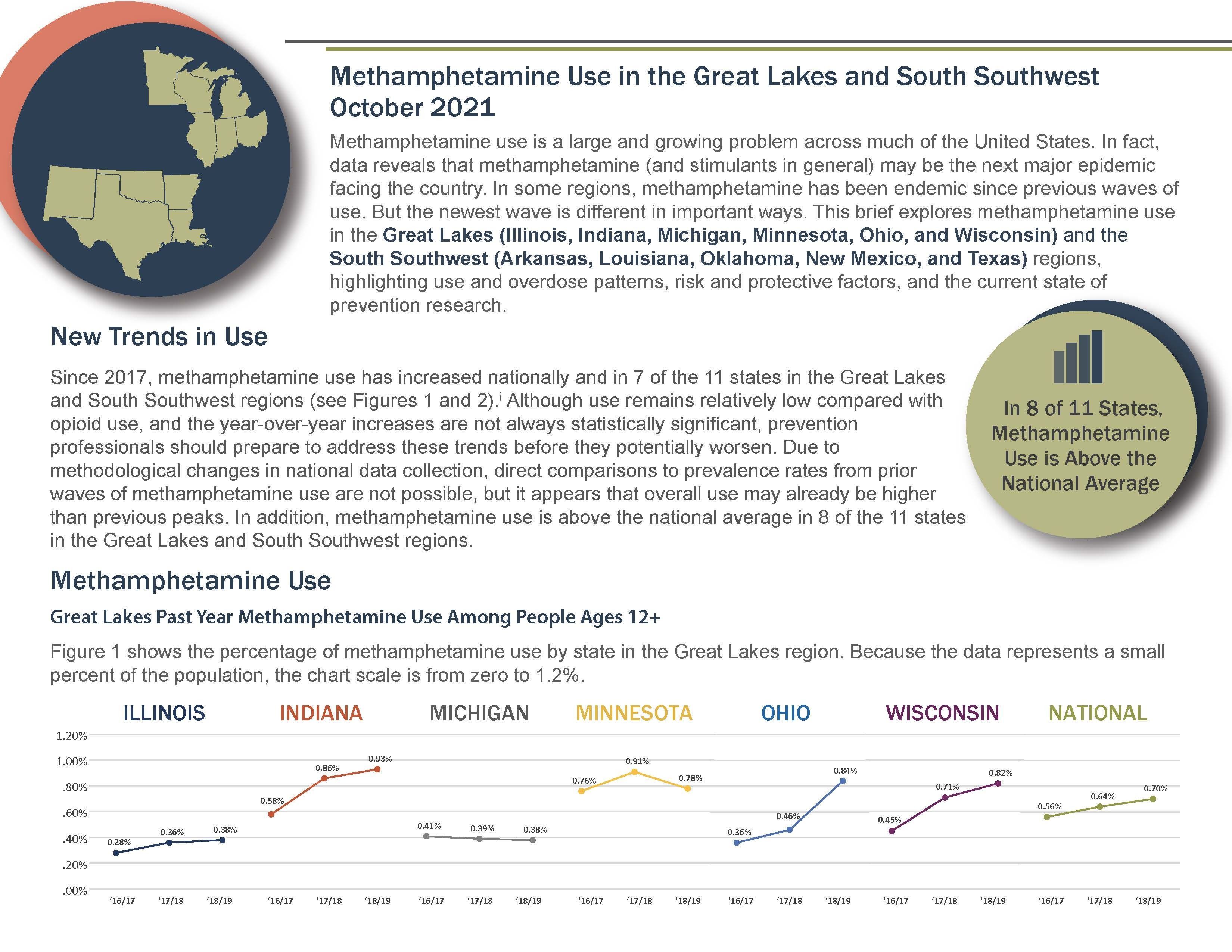
Produced on behalf of the South Southwest and Great Lakes Prevention Technology Transfer Centers, this report highlights the rising use and consequences of methamphetamine in the regions. It also summarizes known risk factors for methamphetamine use and the evidence base for methamphetamine prevention and overdose prevention strategies. Without intervention, methamphetamine may become the next major substance use epidemic in the United States, and appears to already be reaching that status in some places. This report was designed to empower prevention professionals through understanding the scope of the issue in their regions and the need to respond quickly and effectively.
Produced in collaboration with the Central East Prevention Technology Transfer Center (PTTC), this resource guide and literature review present information to support suicide prevention efforts.
The resource guide is a catalog of relevant organizations and tools, at the national level and within the Central East region (DE, MD, PA, VA, WV, and DC). Original publication date: March 2020
The literature review presents the evidence base for the importance for addressing risk of suicide within the context of substance use prevention. It provides information on the linkages between substance use and risk of suicide and provides a reference guide on evidence-based programs for simultaneously addressing both issues. Original publication date: December 2021
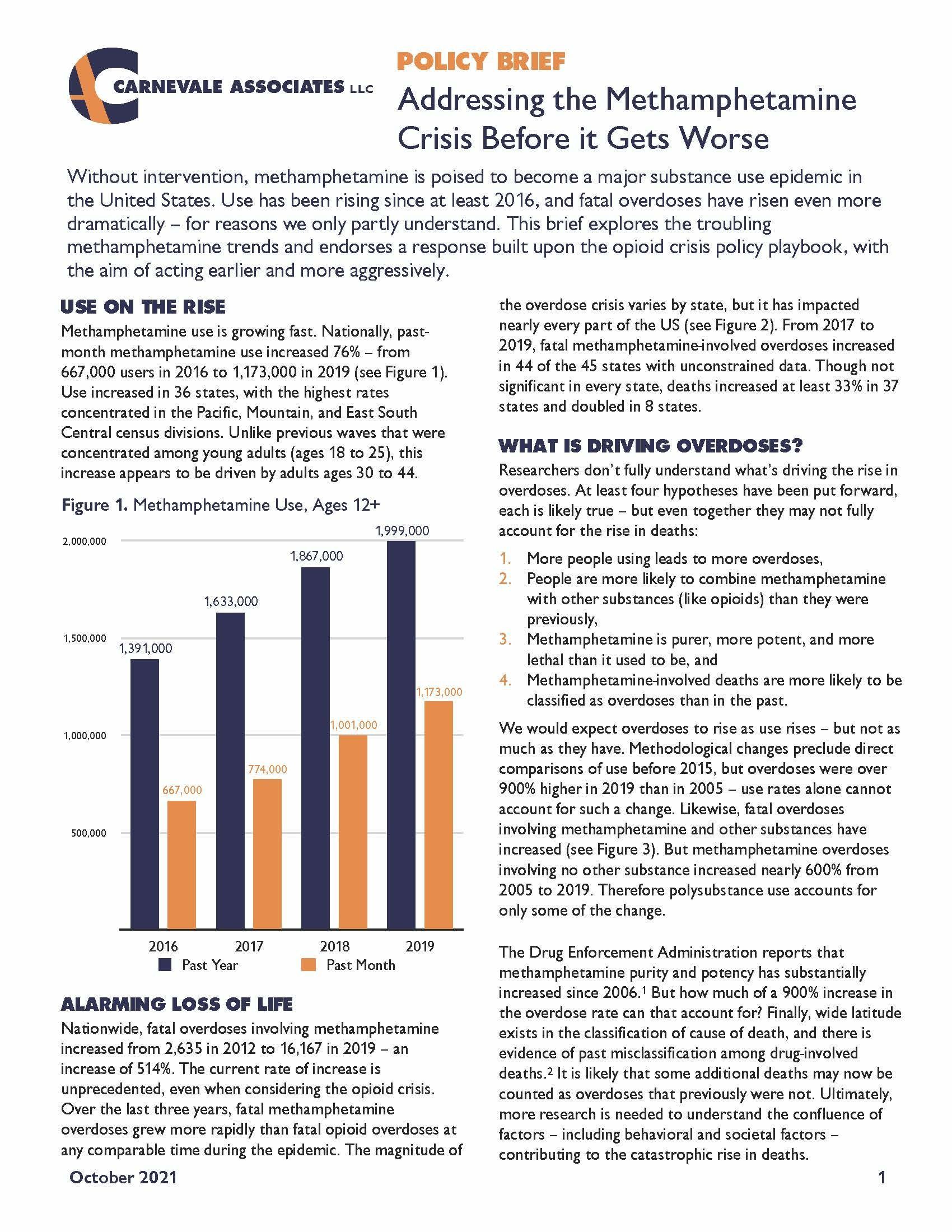
Without intervention, methamphetamine is poised to become a major substance use epidemic in the United States. Use has been rising since at least 2016, and fatal overdoses have risen even more dramatically – for reasons we only partly understand. This brief explores the troubling methamphetamine trends and endorses a response built upon the opioid crisis policy playbook, with the aim of acting earlier and more aggressively.
We have long known that substance use is driven by a complex set of factors and circumstances. Each of our decisions is influenced by our circumstances, consciously and unconsciously. That’s why substance use prevention should be comprehensive – addressing as many of the primary drivers of substance use as possible. Recently, there has been a push to encourage health care stakeholders to focus on how the context of our lives affects our health, notably in the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services’ (HHS) Healthy People 2030 initiative. The factors that comprise this context are referred to collectively as the social determinants of health (SDOH). This brief will explain the SDOH, map the concept of SDOH onto more “traditional” prevention frameworks, and explain how substance use prevention can play a role in such large-scale changes.
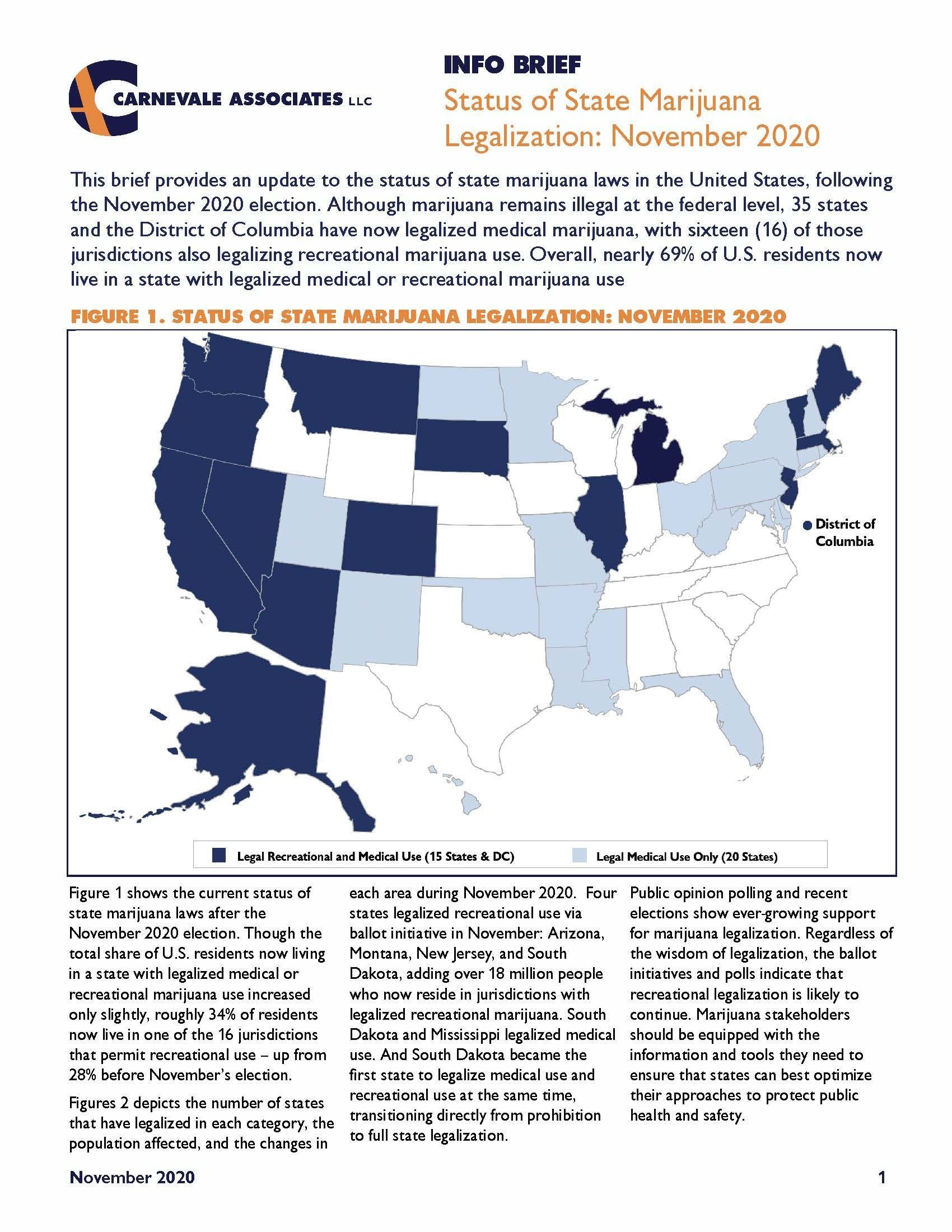
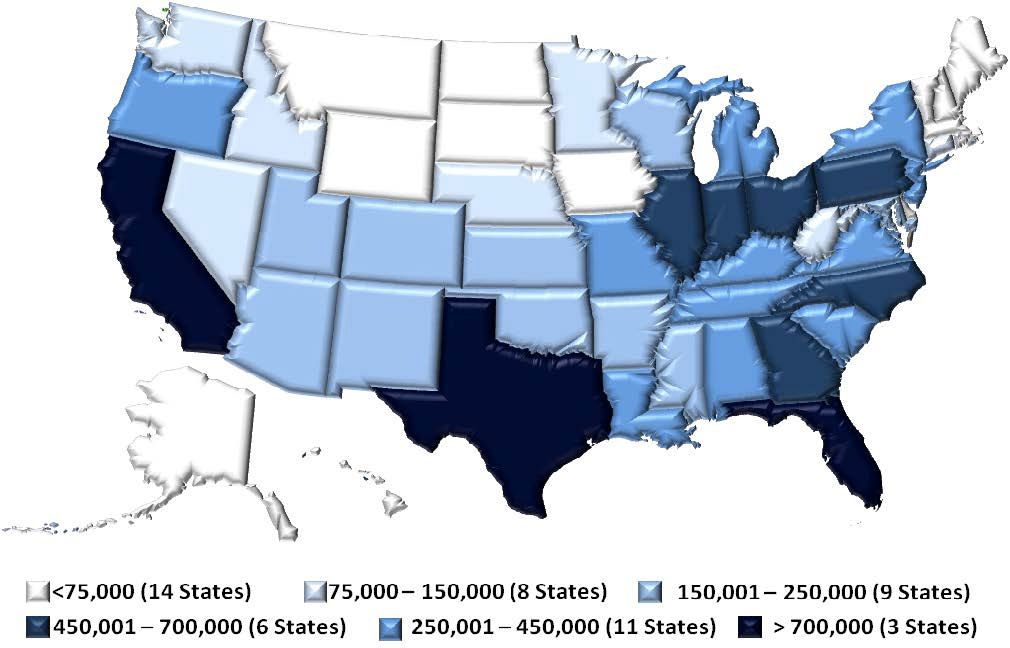
This brief provides an update to the status of state marijuana laws in the United States, following the November 2020 election. Although marijuana remains illegal at the federal level, 35 states and the District of Columbia have now legalized medical marijuana, with sixteen (16) of those jurisdictions also legalizing recreational marijuana use. Overall, nearly 69% of U.S. residents now live in a state with legalized medical or recreational marijuana use.
Jointly produced by several national addiction experts, this comprehensive report contains recommendations and evidence-based strategies for investment of litigation settlement funds to end the opioid crisis and mitigate future harms.
This report was designed to support and empower state and local officials in making critical allocation decisions and consolidates the best research evidence to provide recommendations for high-impact investments that will improve the addiction treatment system, strengthen prevention and harm reduction programming, and address substance use disorder within the criminal justice system. In addition to outlining the scientific support for each recommendation, the authors include detailed guidance related to economic impacts and policy considerations.
A COVID-19 budget crunch is coming, but what will it look like? The Great Recession significantly reduced government revenue and expenditures; behavioral health budgets were cut. But those cuts were blunted by the Affordable Care Act (ACA) and the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA). Current projections suggest the COVID-19 economic downturn will hit government revenue harder than the Great Recession. Reductions in government expenditures are likely to follow, and cuts to behavioral health services may be deep this time without ACA- and ARRA-like provisions. This brief examines the equivalent fiscal elements of the Great Recession to explore the potential effects of the COVID-19 economic downturn on behavioral health services.
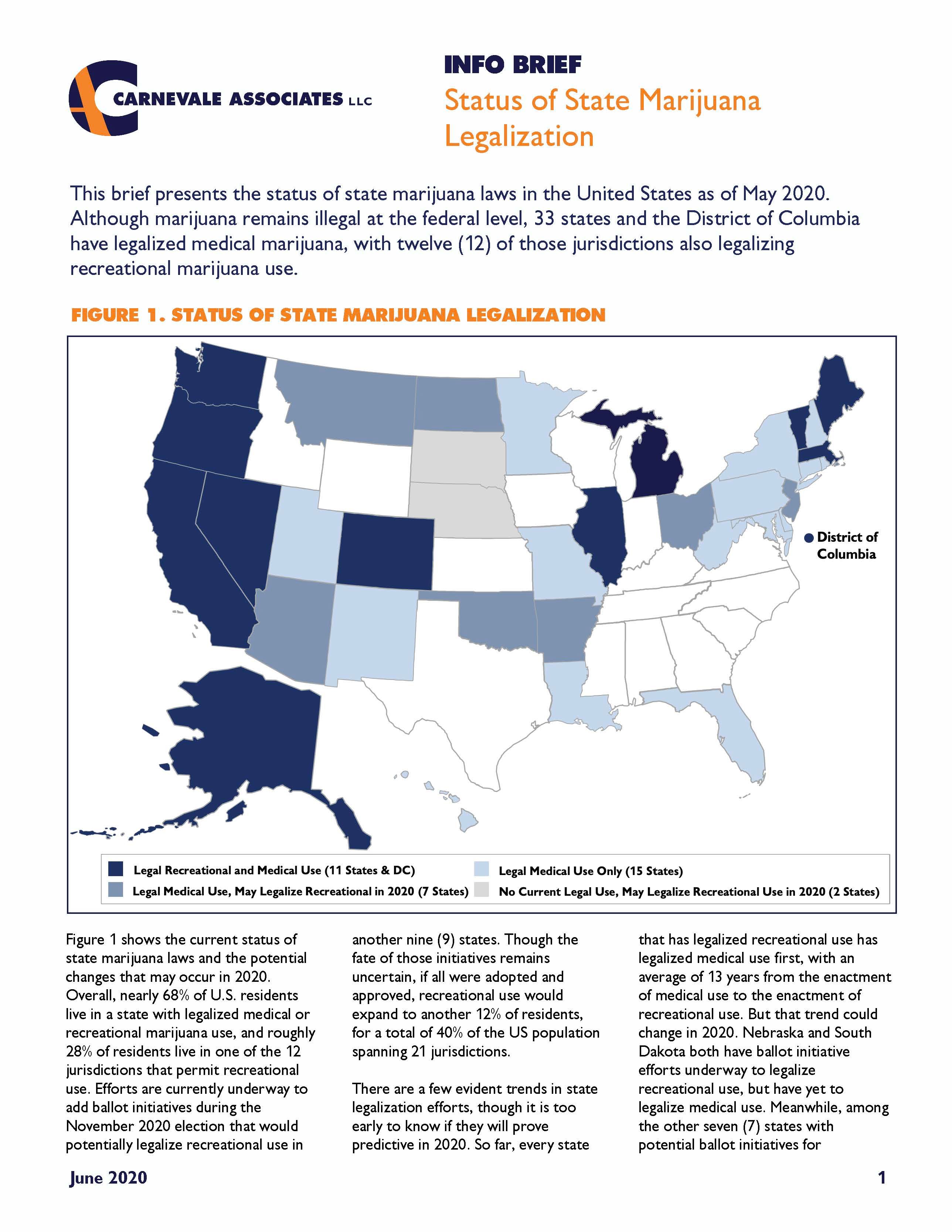
This brief presents the status of state marijuana laws in the United States as of May 2020. Although marijuana remains illegal at the federal level, 33 states and the District of Columbia have legalized medical marijuana, with twelve (12) of those jurisdictions also legalizing recreational marijuana use.
The COVID-19 pandemic is dramatically altering US society. The virus and social distancing measures have disrupted nearly every aspect of life. Prevention professionals must be prepared for disruptions to persist. COVID-19 may increase rates of substance use while hindering the delivery of some prevention services. This brief discusses the short- and long-term need for substance use prevention and offers recommendations on how prevention professionals can safely continue work.
Technology has rapidly revolutionized health care systems, including within behavioral health. Innovative capabilities, such as web-based interventions and smartphone applications (apps), have widespread implications for public health – particularly for the treatment of substance use disorders (SUDs) using evidence-based modalities. This information brief explains the mobile health landscape for SUD treatment, examining benefits & limitations and highlighting the need for further research.
The use of electronic vaporizing devices (“vaping”) among youth presents an urgent challenge. This policy brief explains the popularity of vaping, examines the regulatory environment, summarizes the current public health response, and recommends steps to prevent long-term use and consequences.
This presentation was delivered at the Integrating Primary and Behavioral Health Care Through the Lens of Prevention Conference on November 15, 2018 in conjunction with the Education Development Center (EDC). Carnevale Associates and EDC present on the changing nature of substance use prevention; the shifting health care landscape; health care payers, payment vehicles and service delivery models; and the implications of health care financing for prevention partnerships at both the individual and population health levels.
This presentation was delivered at the National Prevention Network (NPN) Conference on August 28, 2018 in conjunction with the Education Development Center (EDC). Carnevale Associates and EDC present emerging trends in opioids (including heroin and fentanyl), cocaine, methamphetamine, and marijuana -- particularly in the context of substance use prevention.
This presentation was delivered at the National Prevention Network (NPN) Conference on August 29, 2018 in conjunction with the Education Development Center (EDC). Carnevale Associates and EDC outline the state of cannabis laws at the state and local level, review pros and cons of the regulatory options available to states, consider differences between the tobacco and alcohol models of for-profit regulation, and ultimately review the implications of state-level cannabis legalization for substance use prevention professionals.
United States national drug control policy is historically reactive, addressing the latest crisis long after it is established. Prevention is the best policy tool available for addressing emerging drug problems, but it is most effective before problems become well-entrenched. Three emerging trends could prove damaging if ignored: (1) cocaine use by young adults is increasing and cocaine-involved overdoses have exploded, (2) heroin and synthetic opioids are driving opioid overdose deaths, and (3) the country is increasingly accepting of marijuana. In light of these trends, we offer five recommendations to develop prevention infrastructure and facilitate proactive solutions.
This Policy Brief examines the continued expansion of legalized access to marijuana and changes in public opinion in favor of marijuana liberalization. The brief posits that, in light of this extraordinary movement, government at all levels must turn its attention to being proactive rather than reactive by adopting a systems approach to regulating this new industry and designing programs and policies that protect the public health and safety. This brief presents a number of questions that researchers should seek to answer as part of a national research agenda to close the “knowledge gap” between the pace that legalization is occurring and the extent of available knowledge on its potential effects on drug use, public health, and public safety.
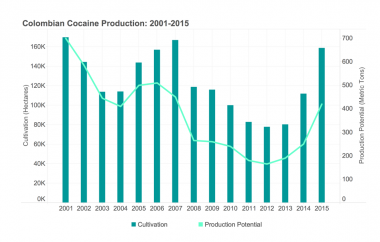
This Policy Brief presents data from the Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) and the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) demonstrating increased coca cultivation in Colombia. The brief questions whether the United States is the target for this new coca, but notes that our diminished ability to detect emerging drug trends renders this an unanswerable question. Ultimately, the brief seeks to raise public awareness of the Colombian cultivation and offers suggestions for improving the detection of emerging drug trends, particularly with respect to cocaine. The brief presents "obvious" next steps -- (1) Funding the Arrestee Drug Abuse Monitoring (ADAM) Program, (2) Restoring ONDCP's Research Funding, and (3) Dedicating Funds for Quest Diagnostic Workplace Drug Testing Data-- as well as more controversial next steps.
On April 7, 2016, the Public Policy Institute of California (PPIC), released a report titled "Regulating Marijuana in California." Authored by Patrick Murphy and John Carnevale, the report concludes that, if California legalizes recreational marijuana, the state should develop a single highly regulated marijuana market-- for medical and recreational uses. The report analyzes the regulatory approaches taken by Washington and Colorado-- the first two states to legalize recreational marijuana-- to help California learn from their experiences.
This whitepaper examines the opportunities and challenges presented by the Affordable Care Act (the ACA) for criminal justice reentry.
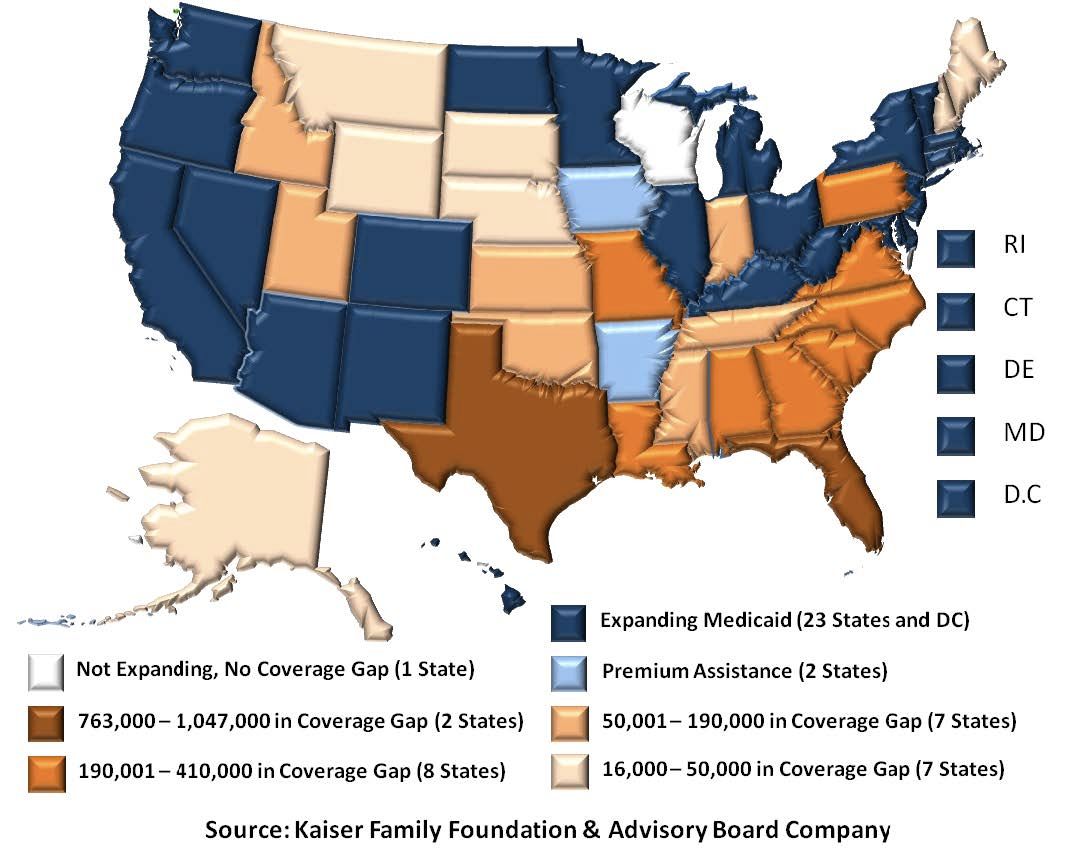
An estimated 6.89 million individuals were under the supervision of adult correctional systems in 2013, 4.75 million under community supervision, 1.57 million in prison, and roughly 731,000 housed in local jails on any given day. With millions more passing through local jails every year, people flowing through the criminal justice system are less likely to have health coverage and often have significant healthcare needs. Yet while the criminal justice system accounts for only a small percentage of the U.S. population, an estimated 14% of residents with HIV, 33% of those with Hepatitis-C, and 40% of those with tuberculosis pass through correctional facilities, while 40% of men and nearly 60% of women in jail have at least one chronic health condition. According to numerous studies, healthcare disruptions when these individuals reenter the community have been found to lead to increased rates or re-incarceration, worse healthcare outcomes, and more costly care.
This Information Brief examines the opportunities and challenges for behavioral health providers under the Affordable Care Act (the ACA). With a particular focus on substance abuse, this brief considers three challenges: (1) The ACA Coverage Gap, (2) Providers' Lack of ACA Knowledge and Strategic Plans, and (3) The Need for Client Outreach & Enrollment. The brief offers solutions to providers' practical problems and calls attention to policy issues that require additional consideration or research.
This Information Brief examines the Affordable Care Act (the ACA)-- also known as health care reform or "ObamaCare"-- and its potential impact on substance abuse treatment. In particular, this brief considers the impact of the ACA's Medicaid expansion, Affordable Insurance Exchanges, and Essential Health Benefits (EHBs) on the healthcare market, anticipating the law's effects on the financing and provision of substance abuse treatment. The brief predicts that the influx of 27 newly insured individuals coupled with EHB and parity requirements will yield a considerable number of new substance abuse clients and trigger a notable shift in payers. These events, in turn, will drive further changes for both substance abuse treatment providers and clients, as the field moves toward new financial systems that emphasize integrated payment models.
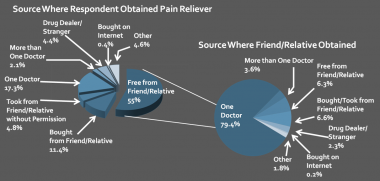
Delivered at the 2013 Utah Valley University Conference on Addiction, this presentation examines the non-medical use of prescription drugs and the Office of National Drug Control Policy's (ONDCP) strategies to curtail prescription drug abuse, notably examining Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PMPs) and the Drug Enforcement Administration's (DEA) Proposed Rule governing prescription drug takeback programs.
Using information retained by the Treasury Enforcement Communications System (TECS) and other sources, Carnevale Assoiciates worked closely with the SAI, the U.S. Department of Justice, National Drug Intelligence Center, and the Department of Homeland Security, Office of Customs and Border Protection, to develop a method for monitoring the quantity of drug-related bulk cash exiting the country each year at ports of entry on the Southwest Border of the United States.
Materials associated with this work are currently FOUO.
This presentation, delivered at the National Conference of Insurance Legislators' (NCOIL) annual meeting in Point Clear, Alabama, examines the non-medical use of prescription drugs (particularly opioids), the consequences of non-medical use, and the strategies currently available to combat such use.
Delivered at the 51st Regular Session of the Inter-American Drug Abuse Control Commission (CICAD) in 2012, this presentation explores the importance and relevance of evidence-based drug policy particularly: formulation, monitoring, and evaluation. The presentation also examines how this policymaking method is more efficient than methods that do not utilize such evidence. The presentation considers general principles of policymaking and explains how to apply those principles to a national drug policy, linking those principles to CICAD's policy framework, which is comprised of: Community, Strategy, Evaluation, and Budget.
Delivered at the 2012 Joint Meeting on Adolescent Treatment Effectiveness, this presentation outlines an ongoing multi-site, four-year evaluation of the Juvenile Drug Court (JDC) and Reclaiming Futures (RF) Initiative. Under the initiative, juvenile drug courts integrate the 16-element JDC model with the 6-step RF model.
This 2012 presentation highlights current trends in prescription drug abuse and potential policy solutions.
This Policy Brief examines prescription drug takeback programs in the context of substance abuse prevention. Across America, drug takeback programs have become increasingly popular as policymakers struggle to provide individuals with a secure and convenient way to dispose of unused medications. To learn more about takeback programs, Carnevale Associates, LLC surveyed a number of programs to better understand their design, costs, and efficacy to support national efforts to reduce the size and scope of the prescription drug epidemic. Our analysis found that these programs vary substantially in cost and approach. In addition, we found no evidence that takeback programs affect prescription drug abuse. We conclude that additional research is needed before incorporating takebacks into any substance abuse prevention plan.
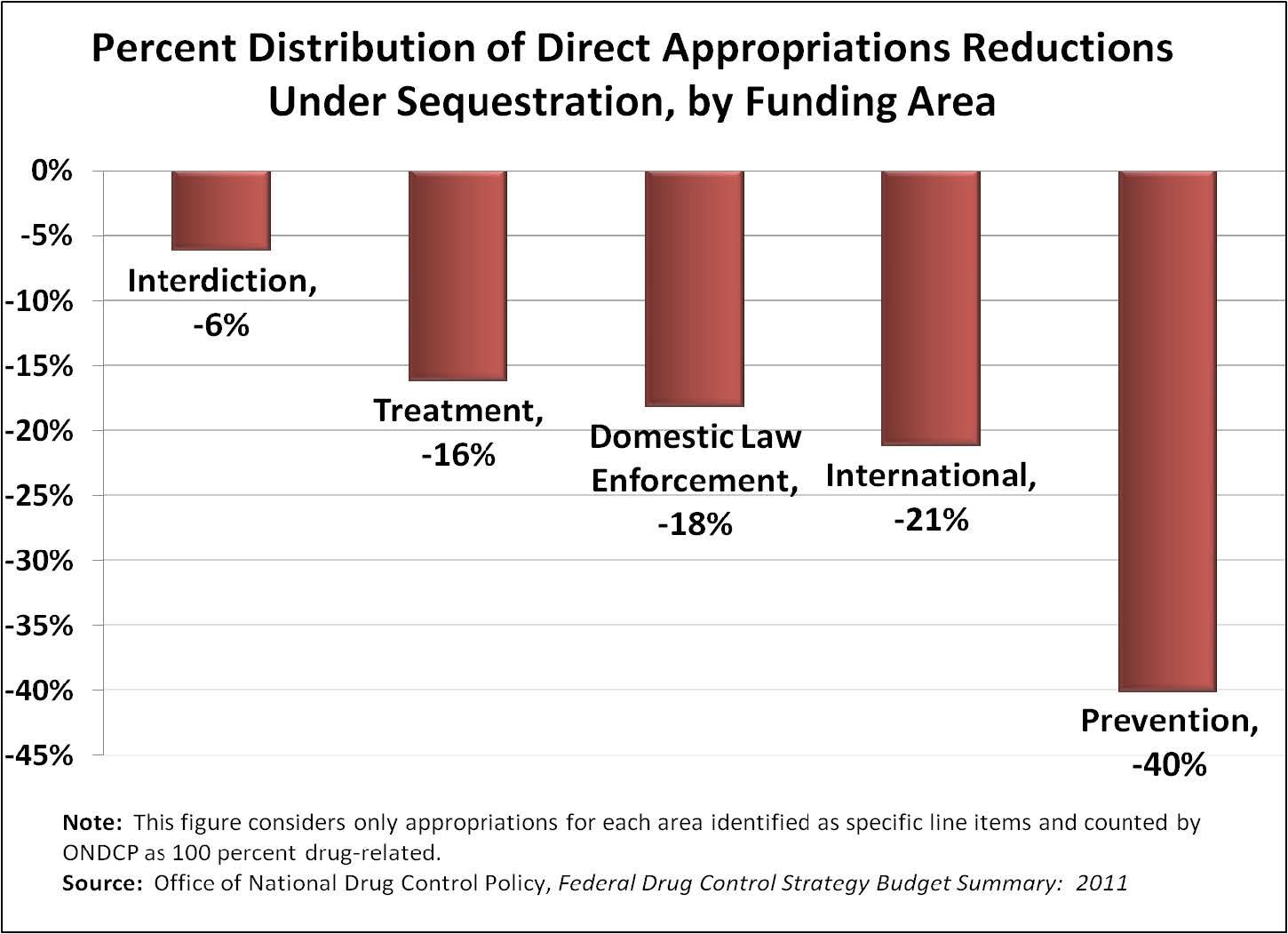
With the failure of the Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction to reach an agreement, this Policy Brief examines the effects of a $1.2 trillion sequestration (automatic cut) on the federal drug control budget. Slated for implementation beginning in 2013, Carnevale Associates' analysis finds that the proposed cuts would be much more detrimental to demand reduction programs than to supply reduction programs. The disproportionate impact on demand reduction programs may impede the Obama administration’s stated aim of implementing the public health approach promoted in its National Drug Control Strategy.
Delivered at the National Prevention Network (NPN) Conference in Atlanta, GA on September 22, 2011, this presentation created for the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration's (SAMHSA) Center for Substance Abuse Prevention (CSAP) under the Data Analysis Coordination and Consolidation Center (DACCC) explores ways to use prescription drug monitoring programs (PDMPs) to inform substance abuse prevention policy and decision making.
This Policy Brief examines the present state of prescription drug abuse and the potential role of Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs or PMPs) in providing real-time information to inform prevention, treatment, and law enforcement policies, programs, and practices.
This 2011 U.S. Department of Justice National Drug Intelligence Center report-- prepared by Carnevale Associates, LLC. and Simeone Associates, Inc.-- examines the economic cost of illicit drug use in America, concluding that such use cost the U.S. $193 billion in 2007.
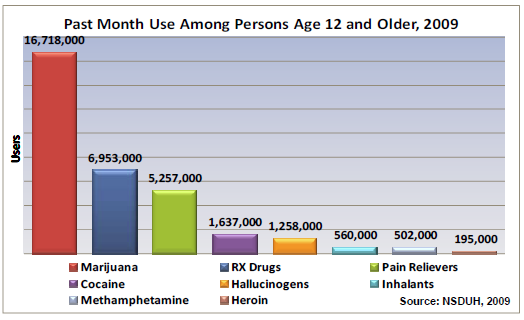
This Policy Brief examines recent data implying that the methamphetamine epidemic is rebounding after several years of decline. Exploring the relationship between current trends and existing laws, this brief offers policy solutions for prevention, treatment, and law enforcement.
This Policy Brief shows what can happen when a drug policy fails to align program resources with its strategic goals and objectives.
The Brief shows that the nation has experienced a standstill in progress to reduce drug use so far in this decade and attributes this lack of progress to the eight-year failure of the Office of National Drug Control Policy (ONDCP) to meaningfully match its federal drug control budget with the demand reduction goals set forth by its own policy.
This Policy Brief raises the strong possibility of a resurgence in youth drug use. While youth drug use declined by 29 percent from 1997 to 2006, a recent softening of indicators related to youth attitudes about the dangers of drug use and disapproval rates suggests that drug use is making a comeback.
The previous administration cut funding for drug prevention programs which might have contributed to this softening of youth attitudes about the dangers of drug use. Further cuts to drug prevention programs are proposed in the federal 2010 budget.
This 2009 Information Brief examines Salvia Divinorum ("Salvia") as an emerging drug trend. The strongest naturally occurring hallucinogen, this brief examines Salvia's effects and use patterns, noting that past year Salvia use outpaced both LSD and PCP in 2006.
This 2008 Policy Brief highlights the principles of an effective national drug control policy, emphasizing the importance of research-based approaches and the need to link strategy and budget.
This 2008 Policy Brief reviews the federal drug control budgets from FY2002 to FY2009, concluding that the budget did not fund programs that research suggests would be most effective in reducing drug demand and its associated damaging consequences. Examining spending data for the decade, the Brief concludes that the federal drug budget trend ran counter to what research would otherwise suggest is necessary for an effective federal drug control policy, emphasizing interdiction and source country programs over treatment, prevention, and domestic law enforcement.
Examining research by Simeone and Holland (2006), this 2007 Information Brief examines Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs (PDMPs), demonstrating that PDMPs are effective at both limiting drug supply and reducing the probability of prescription drug abuse. The findings also suggest that proactive monitoring programs-- those that generate unsolicited reports to identify and investigate cases-- are more effective at reducing drug supply and potential abuse than their reactive counterparts, which generate reports only in response to third party requests.
This 2007 Policy Brief examined the Office of National Drug Control Policy's (ONDCP) proposed drug budget for FY2008, noting the sharp decline in funding for prevention programming.
The brief contends that the FY2008 budget trend goes against well-established principles of effective drug control policy, including the need for a comprehensive balanced approach between interdiction, law enforcement, overseas programs, and prevention and treatment programming. Specifically, the Policy Brief notes that the FY 2008 budget request continues the Bush Administration’s long-term trend of shifting resources away from demand reduction (treatment and prevention programs that seek to discourage individuals from trying illicit substances or help existing drug users stop using) toward supply reduction (programs that attempt to stop the flow of drugs entering the country or disrupt domestic drug markets).
This 2005 Information Brief examines the Program Assessment Rating Tool (PART) and its effect on the FY2006 federal drug budget. Comparing federal drug programs' PART scores for FY2005 with the FY2006 proposed funding allocations, the Brief found that program's PART measurements did not appear to be in sync with their FY2006 funding.